Drain back solar hot water systems are one
of the most common types of solar thermal systems used today. In short, they utilize
two temperature sensors to control the system. When rising temperatures are
detected in the solar collectors, cold water from the storage tank is pumped
through, absorbing heat as it’s pushed through. The water then flows back into
the drain back tank to maintain a certain temperature.
Drain back solar hot water systems can be
designed a few different ways:
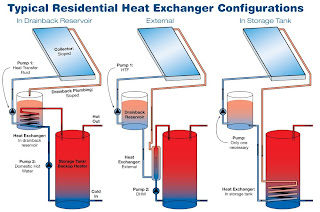
Type 1 drain back design, often called a
two-tank system, uses a full size solar hot water storage tank, and a separate
solar storage tank. This design can be used for large or small systems. When
hot water is used in the home, it passes through the heat exchanger into the
hot water heater, preheating the water and minimizing the energy used by the
regular water heater.
Type 2 drain back design uses a solar hot
water heater with a built-in heat exchanger. This one-tank system uses one pump
to run the collector loop, and holds the volume for solar storage and for the
regular hot water heater. They are used mainly for smaller residential systems.
Type 3 drain back design is used for
similar applications, and has a heat exchanger located within a small reservoir
tank, making it compatible with gas or electric conventional hot water heaters.
A second pump is usually needed to circulate water within the system.
The advantages and disadvantages of each
system design vary by application. Depending on your home and the configuration
required, one solar hot water system design may offer better results and more
energy savings. The experts at Smith Sustainable Design will plan your solar
hot water system design using the most appropriate configuration for your home.
If you have questions about the drain back options available, please give us a
call.

No comments:
Post a Comment